Panasonic’s proprietary low spatter control, developed over many years, reduces post welding processes
This page introduces low spatter control on Panasonic welding machines and robots.
This is our proprietary electronic reactor born during the development of our V series full-digital welding machines. They achieve high-speed control of welding current waveforms. Full software control makes welding pleasant over the entire current range, from low to high current, and greatly reduces the amount of spatter.

The encoder motor equipped to the wire feeder and the dedicated feed control CPU built into the welding power supply communicate with each other to provide constant wire feed. Compared to analog power sources, the feed rate is not affected by input voltage fluctuations and wire feeding load fluctuations.
MTS control (MTS-CO2)
MTS control is an abbreviation for Metal Transfer Stabilization Control. It opens the short circuit and reduces the vibration of the molten pool when the arc is rearced. It also suppresses micro-shorts during the arc period.
The first difference between the conventional CO2 method and MTS-CO2 droplet transfer is the initial short circuit. Short circuits are detected with high accuracy, and secondary switching*1 sharply reduces the current to prevent micro short circuiting (spatter generation), and then transitions to a reliable short circuit. (Initial short circuit control)
Wire tip nicks are also detected and the current is rapidly reduced by secondary switching to prevent the fuse effect (spatter generation) at the wire tip. (Neck control)
*1: Secondary switching is a control method to reduce spatter by dropping the welding current sharply immediately before and after a short circuit to smoothly transition to a short circuit or arc.

Welding current: 200A, Voltage: 22.0V, Welding speed: 40 cm/min
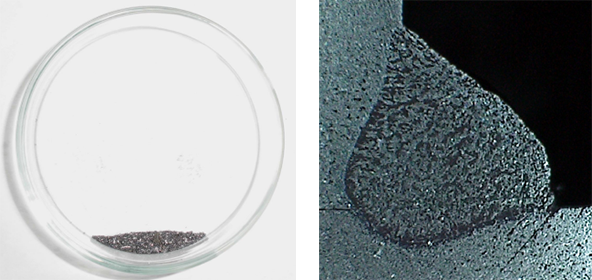
New MTS control
In addition to the above MTS control, waveform control strengthens the arc force during the arc period, thereby reducing micro short circuits that occur during the arc period and achieving even lower spatter.
Welding current: 200A, Voltage: 22.0V, Welding speed: 40 cm/min


SP Control (SP-MAG)
Initial short circuit control and neck control are the same as MTS control, but the current is superimposed immediately after short circuit opening to increase the melting rate of the wire tip to make the next short circuit smoother and the short circuit cycle is controlled to be shorter (T0 → T1).

New SP Control
The new SP control is the addition of a hybrid electronic reactor to the SP control. This optimizes the current waveform and provides the following benefits:
- Optimized welding waveform significantly reduces spatter
- High resistance to changes in welding posture and low influence of torch angle
- Brief short-circuit cycle, ideal for high-speed welding
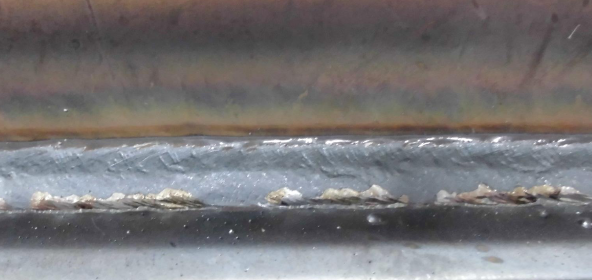
Base metal: Mild steel (thickness: 2.3 mm) Joints: Fillet weld Welding current: 130 A 16.8 V Welding speed: 30 cm/min Wire: YM-50MT (1.2 mm) Gas: MAG (Ar 80% + CO2)
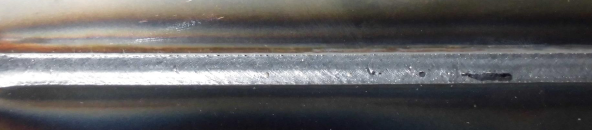
Base metal: Mild steel (thickness: 3.2 mm) Joints: Fillet weld Welding current: 190 A 18.4 V Welding speed: 30 cm/min Wire: YM-50MT (1.2 mm) Gas: MAG (Ar 80% + CO2)

Base metal: SUS304 (thickness: 1.5 mm) Joints: Fillet weld Welding current: 110 A 14.4 V Welding speed: 30 cm/min Wire: Y308LSi (1.2 mm) Gas: MIG (Ar 98% + O2)

Base metal: SUS304 (thickness: 3.0 mm) Joints: Fillet weld Welding current: 160 A 16.2 V Welding speed: 30 cm/min Wire: Y308LSi (1.2 mm) Gas: MIG (Ar 98% + O2)

This page introduces the power source control method, which is the core of the welding machine, in addition to its evolutionary changes.

This page introduces pulse control, which realizes high-precision welding.
Panasonic has established a system to support customers all over the world. Customers expanding production from Japan to overseas factories can also use our equipment with peace of mind.

Website dedicated page for members of Panasonic Shoyokai. You can download the application form to join the membership website P-Web.
